With the development of photovoltaic inverter technology and the improvement of efficiency, the heat dissipation form has changed from the initial cooling of all fans to the following three mainstream heat dissipation designs.
1. Integrated die casting mold fanless design
Advantages: First, the upper and lower parts of the mold shell integrated heat dissipation, not only greatly increased the heat dissipation area, but also greatly reduced the heat transfer impedance; Second, the internal heat source device can be an excellent heat dissipation, both to ensure that the heat balance inside and outside the inverter, but also All kinds of devices are in the best working condition.
Disadvantages: For products with high power density and fanless design, customers have misunderstandings. The lack of heat dissipation of the device is believed to result in reduced power generation and affect inverter life.
Representation model 1: H manufacturer inverter. The internal temperature of the inverter is the same as the temperature of the chassis enclosure. At an ambient temperature of 45 degrees, the internal temperature is approximately 55 degrees.
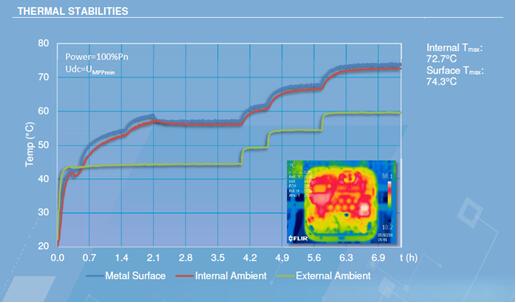
Representative model 2: Y manufacturer inverter. The internal temperature of the inverter is the same as the temperature of the chassis. At an ambient temperature of 45 degrees, the internal temperature is about 60 degrees.
Option 2: General External Fan Design
Advantages: The chassis surface temperature is low.
Disadvantages: The inverter heat sink has a small size. Although some heat of the internal heat source device can be carried away by the fan, the heat dissipation of the entire heat source device is not uniform. Not only that, the inverter also has the problem of high heat dissipation resistance of the external cabinet and internal heat source devices, and the internal heat is not easily transmitted to the surface of the chassis, so that the temperature of the internal components is much higher than the surface of the chassis, which may result in equipment derating or internal devices. Reduced long-term heat life;
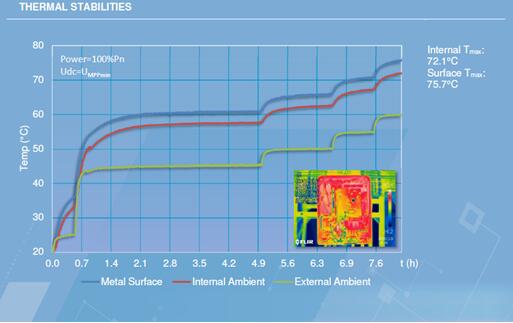
Representation model 1: S manufacturer inverter. The internal temperature of the inverter is 15 degrees higher than the temperature of the chassis case. At an ambient temperature of 45 degrees, the internal temperature is about 65 degrees.

Representative model 2: S-inverter. The internal temperature of the inverter is about 15 degrees higher than the temperature of the chassis case. At an ambient temperature of 45 degrees, the internal temperature is about 70 degrees.
Scenario 3: General sheet metal fanless design
Advantages: The internal heat flow exchange design can quickly transfer the heat flow of the internal heat source device to the inverter surface;
Disadvantages: The shell is designed for non-die casting molds, and the heat dissipation resistance and heat dissipation area are inferior to the die casting mold products. Not only the surface temperature of the inverter is high, but also a larger radiator (increasing the volume of the chassis) is used as support.
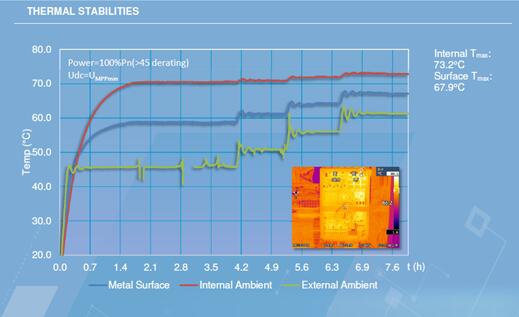
Representation model 1: G manufacturer inverter. The internal temperature of the inverter is about 15 degrees lower than the case temperature of the chassis. At an ambient temperature of 45 degrees, the internal temperature is about 55 degrees, but the surface temperature is as high as about 75 degrees.
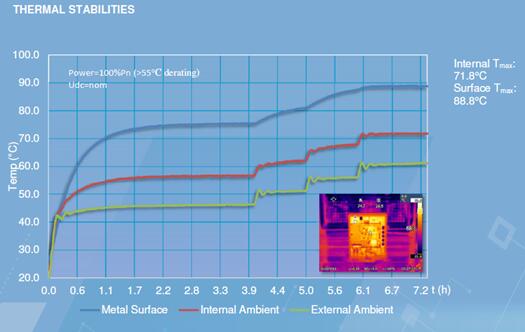
Conclusion: It is not difficult to find through the above analysis and data that the fanless design of the inverter (as shown in Scheme 1 and Scheme 3) has a significantly higher surface temperature than the fan design, and this temperature can often reach 60 degrees. But do not worry that it will cause fire because it is hot, because it is only the temperature of the outer box (60 degrees outside the box is the normal working range of the fanless design inverter), and the internal temperature of the device is lower, so use this The design of one is to ensure the life of the device and the power station to run without derating and ensure the power generation; look at the inverter shown in Scheme 2, which is typical of a lower surface temperature corresponding to a higher internal temperature. One can imagine, Operating the device in such an internal environment will reduce inverter life.
















 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite







